Review
Summary
Clarity about is important for all, not just for scientific practitioners. In everyday life, unsatisfactory can lead to endeavours being pursued on false premises with substantial losses and personal or social harm.
The research community as a whole now depends on government financial support and general social support. As a result, the ultimate value of truth is in danger of evaporating or being subordinated to political necessity and financial imperatives. Maintaining a clear fix on the value and rationale of each of these 7 fundamental may potentially assist in the re-assertion of essential values.
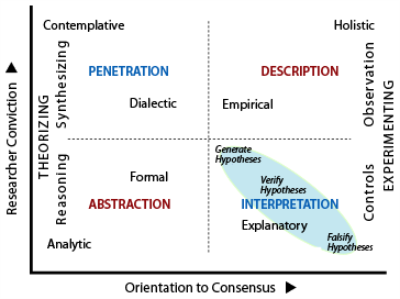
The Table below summarizes the TET findings and restates the core principle and rationale of the method. Click on the row and column headings for more details.
Better viewing: Use browser zoom if needed.
| L' | Research Method | Core Principle | Consensus & Findings |
Conviction & Communic'n |
Auspices | Mental Operations | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L'7 | Contemplative | Speculate insightfully |
Independent & possible |
Compulsive & illuminative | Personal | Synthesizing via penetration | To alter a current belief system. |
| L'6 | Formal | Reason mathematico-logically | Relevant & persuasive |
Impartial & explicative |
Personal | Reasoning via abstraction |
To ensure absolute precision. |
| L'5 | Holistic | Model systems completely | Controlled & probable |
Compulsive & illuminative | Personal | Description via observation | To facilitate deliberate change. |
| L'4 | Dialectic | Address polarization | Relevant & persuasive |
Directive & asseverative |
Collegial | Synthesizing via penetration | To unify knowledge & unite inquirers. |
| L'3 | Explanatory verification |
Test hypotheses |
Dependent & plausible |
Supportive & stimulative | Collegial | Interpreting via controls | To establish causal relations. |
| Explanatory falsification |
Test hypotheses |
Controlled & probable |
Impartial & explicative |
Personal | Interpreting via controls | To establish causal relations. | |
| L'2 | Analytic | Ratiocinate systematically | Independent & possible |
Supportive & stimulative | Collegial | Reasoning via abstraction |
To offer a reasoned base for inquiry. |
| L'1 | Empirical | Accumulate facts | Dependent & plausible |
Directive & asseverative |
Collegial | Description via observation | To remain fully grounded. |
Application of Methods
Settings
are used repetitively on particular topics within settings (disciplines, institutions) specifically dedicated to inquiry. The setting and topic have significant effects on the choice of method. However, using any in a single study produces findings not knowledge. ![]() More
More
Academic disciplines can be divided into the foundational disciplines (philosophy, mathematics, systems), the humanities and the sciences.
All substantive disciplines use a number of methods because the subject matter needs scrutiny from different perspectives. How the method-based perspectives are combined to generate knowledge will be examined in relation to the Spiral transformation.
Theme-based Cross-Disciplinary Studies
Studies that focus on a theme from social life—water, waste-disposal, welfare, national security, environmental protection &c—involve multiple disciplines.
Multi-disciplinary teams or specialized institutions are set up to enable any and every method. If there is a need to weld distinct disciplines with divergent loyalties and career paths, then uniformity of method may be needed.
Being inherently socio-physical and change-focused, the is often requisite.
Reflection
Q: What form of inquiry is used to produce this taxonomy?
A: The method being used is because the goal is to model a system completely. ![]() More
More
Further Thoughts
- Inquiry terminology.
- Influences amongst methods.
- Compare and : more on realism v idealism.
- Reflections on THEE and Scientific Method.
- Comparing methods in social science.
Originally posted: 28-Aug-2015. Last amended 21-Feb-2022.