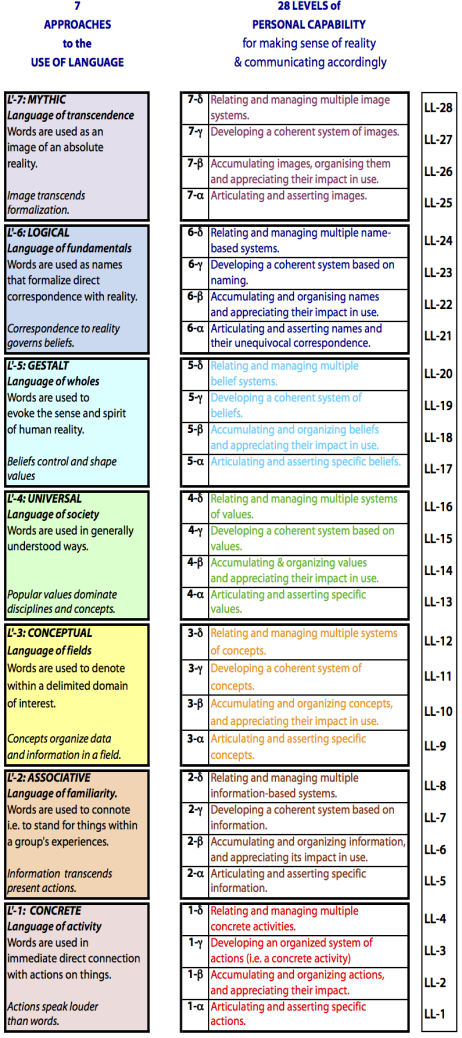
28 Levels of Language Use
Using Language at Work is a Public Matter
As explained, involves making sense of reality in a consistent way so as to have confidence about being for altering it. This «making sense» is about interacting effectively, not simply holding a private belief.
You have to be able to persuade yourself and others to act on what you see. This is especially evident in organizations where people work in teams within and across levels.![]() More
More
Remember: show an internal duality in which work at the lower 4 Levels requires in one approach, and work at the upper 3 Levels requires in the next higher approach. This 7-Level system in THEE is labeled a Q-hierarchy: and the earliest inquiries focused (unknowingly) on the second in the series: QH2.
These Q-hierarchies identify distinct in society: as explained here.
 Formulating Work Responsibility
Formulating Work Responsibility
has been located in the Q-expansion of the within the .
![]() So some familiarity with the use of language framework (currently in the TOP Studio) is beneficial in appreciating the analyses here and in future sections.
So some familiarity with the use of language framework (currently in the TOP Studio) is beneficial in appreciating the analyses here and in future sections.
Development of this part of the taxonomy requires:
- determination of the Levels in the Style Hierarchy (formerly called a Modal Hierarchy).
- application of these modal Levels (Styles) to the Principal Typology by determining the aspect of language that comes to the fore in each .
- determining 7-Level Q-hierarchies by combining a complete 4-Level Approach with the lower 3 Levels of the next higher Approach. (This taxonomic system is cyclic with L'1 being regarded as higher than L'7.)
- naming the 7 Q-hierarchies and developing Frameworks derived from them like Trees and Structural Hierarchies.
- appreciating interactions between Q-hierarchies.
-
Alternatively, consider additional Q-arenas beyond formal organizations.
Originally posted: 25-Oct-2013