How Change Happens
Actions or Ideas
Change depends on the use of both actions and ideas. ("Ideas" includes theories, information, knowledge &c).
Each paradigm has its own assumptions and preferences as to whether action or ideas should be most significant and trusted in determining change.
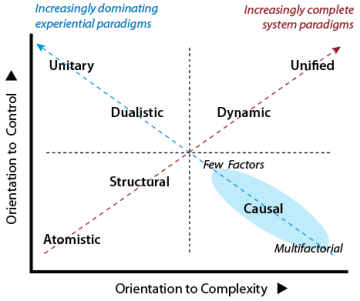
The analysis below in terms of the experiential v system approach duality reveals a pattern:
» experiential paradigms prefer action,
» system paradigms prefer ideas.
Experiential Paradigms prefer Action
The paradigms on the diagonal moving from LR to UL seek domination and value action above ideas. The preference increases as the diagonal is ascended.
The values action because that is the source of all causation and the ultimate method of delivering benefits. Ideas and reasoning are valued guides to action but must be handled flexibly. Records may be kept to monitor action and outcomes.
The favours action, and views ideas and theories sceptically. Opposing ideas may be promoted by the two protagonists, but evidence that does not support a chosen view is commonly ignored or denigrated. Rational arguments against a value-based position are handled using emotional language, ambiguity, ad hominem attacks, red herrings and other logical fallacies. The ultimate goal of the two opposing participants is to dominate and win the argument not to use discussion or debate to help determine the most suitable course of action.

The sees action as primary, because that is the ultimate source of power. Ideas are used as powerful weapons, not as the basis for knowledge, helpful communication or rational debate. Within the situation, ideas are used for social control and are inculcated via indoctrination and propaganda. Lying and deception are regarded as normal practices to handle both insiders and outsiders. thinking regards it as appropriate to use torture or inflict suffering to extract confessions even though these have no validity.
System Paradigms prefer Ideas
The paradigms on the diagonal moving from LL to UR recognize that action is the final common pathway for change, but regard information and ideas as critical for desirable and effective action.
The regards action as an essential expression of personal autonomy. The right and responsibility to determine what actions serve personal interests implies the necessity to reflect on interests and preferences prior to action. There is also a tendency to speculate, which is unchecked by others and therefore likely to be idiosyncratic.
The values information as essential to component definition and rule-based operation. The ordering of the entity typically specifies functions, goals and rules, which control action in principle. Ordering also ensures action is regulated in accord with data flows and provision of simple feedback loops.
The views all action as ideas-based. Decisions are generated by values and purposes, which should generally be shared and discussed. Courses of action generate evolution and take into account the views of those involved. Results are subsequently reviewed via feedback.
The leads to extremely complicated theories which include intrinsically ethical concerns and potentially spiritual perceptions. Mastery of a developed framework helps to ensure that actions will not be counter-productive. Growth is based in handling co-evolution in accord with that thinking.
With this background, we can now consider:
- how thinking styles vary according to the .
Originally posted: 30-Jun-2024. Last amended: 15-July-2025.
