Control of Change
![]() This webpage provides a quick summary and technical overview of the key structures and concepts that will be developed and referenced in this section.
This webpage provides a quick summary and technical overview of the key structures and concepts that will be developed and referenced in this section.
The Spiral Complex
Following THEE principles, the in the are alternative methods of control for optimizing use of the fundamentals in the . They do this by guiding the use of , the Domain Vehicle that so as to enable a , which is the Domain Field.
This graphic lays out the fundamentals in the :
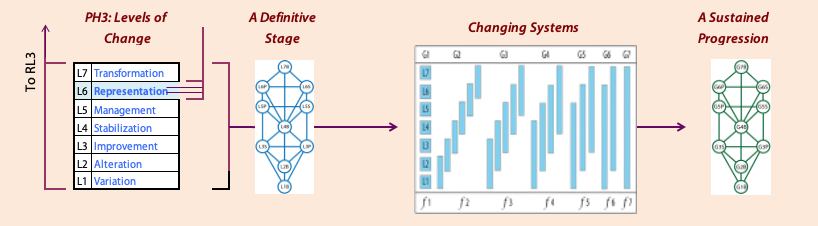
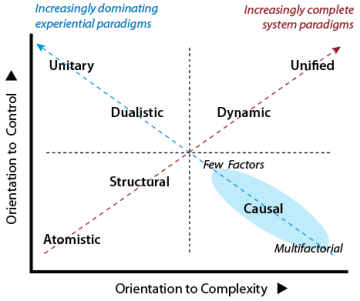
The can be holistically viewed and appreciated using a TET diagram as presented in the previous section and shown at right. The TET axes for handling complexity (X) and seeking control (Y) form the psychosocial context when handling any .
While the are distinct and incompatible, some assumptions and principles within each of the methods are widely shared values. By abstracting these values and converting methods for proceedingto modes of functioning, it is possible to combine them. Combination is developed by progressively cumulating modes to generate a developmental Spiral on the TET. This Spiral, in turn, reveals additional control mechanisms.
Any Spiral Control Complex specifies essential Domain features, the most important of which are:
-
Psychosocial Pressure
Each Root Level defines a Primary Domain and carries a psychosocial pressure which has a neuro-biological origin and can be irresistible in practice.In the case of , the psychosocial pressure is conjectured to be Acceptability.
-
Primal Need
Each Domain exists to meet a instinctive vital need, the primal need, essential for personal survival. The need is handled by the Domain Fundamentals.In the case of , this need is conjectured to be in the sense of any change the relevant socio-physical environment, and the person relevant groups.
All Domain Fundamentals (i.e. and any ) are therefore evaluated in terms of their .
-
Primal Means
Controlling Domain Fundamentals, there is a specific primal means that plays a major role in meeting the primal need and can operate with varying degrees of sophistication according to a person's (or group's choice.In the case of , the primal means to enable is conjectured to be .
requires about situations as a core psychic state around which in general can operate. Because is a continuing requirement for social existence, the degree and quality of is directly relevant to maintaining acceptability.
-
Primal Controller
The primal means is itself subject to control by Requirements associated with and responding to the Domain's psychosocial pressure: acceptability.The is currently conjectured to be . This puts under a pressure for acceptability with the goal of reliably ensuring a person's psychosocial .
The proposed relation between the and the Domain Controls for is shown in the diagram below:
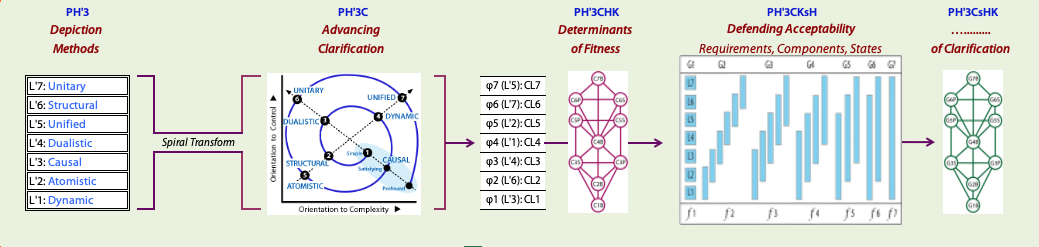
See Taxonomy Notes for provisional outlines of the structural hierarchy and its tree.
Originally posted: 30-Oct-2024. Last amended: 20-Apr-2025.
