Marketing Strategies: 4thSet
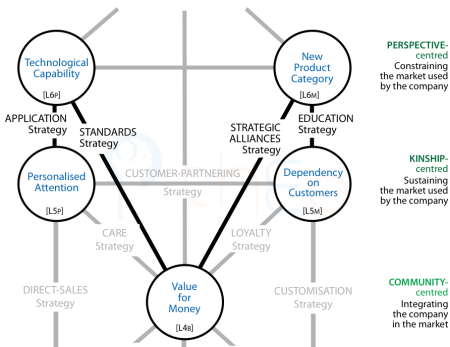
L6P ↔ L4B
| L6P Focus: | Technological innovation |
| L4B Focus: | Strategic benefits for customers |
Notes:
- Revolutionising the way the world does something is inherently visionary. Such change in end-user behaviour depends on technological discoveries that enable new concepts, breakthrough innovations, ultra-efficient infrastructures and simple but powerful tools.
- Customers cannot benefit from such revolutionary changes unless the necessary support is available, and this depends on institutionalisation of enduring standards.
L6P ↔ L5P
| L6P Focus: | Power of a new technology |
| L5P Focus: | Visionary customer |
Notes:
- New applications enable a previously unavailable strategic capability that provides a dramatic operational advantage. However, relatively few customers can see the possibilities or are prepared to put in the effort and take on the risks.
- The customer is involved in specifying the application and in providing considerable input into its development. Customers require encouragement to persist and overcome difficulties, and the whole process is time consuming. On-site service/training can provide supportive remuneration.
L6M ↔ L4B
| L6M Focus: | Practical implications of a new idea |
| L4B Focus: | Feasibility for the customer |
Notes:
- Useful new product ideas typically require the introduction of supporting products or services from either other businesses or government agencies. The alliance must be essential for the partners—not just another convenient operational arrangement.
- Feasibility may also relate to the purchasing psychology; alliances may provide essential marketplace clout, help reach critical price targets and build customer confidence.
L6M ↔ L5M
| L6M Focus: | Desirability of the new |
| L5M Focus: | Customer acceptance |
Notes:
- Until customers feel that they must have the product, it will not sell widely. It can either be indispensable for functional reasons or highly fashionable (for obscure reasons).
- Credibility is the key to acceptance. People may accept something new if it is used by role models, promoted via free samples or trials or associated with desirable situations. If the product is technical, then methods include advertising which teaches, explains and informs; trade shows; magazines and awards; user journals; conferences; press releases; and educational programs for newspapers, periodicals, television and radio.
-
Continue with strategies that activate realistic anticipation (L7), innovation (L6) and dependency on customers (L5).
Originally posted: July 2009
